EEG Virtual Amplifier.
The idea of the Virtual Amplifier has arisen because there was a need to simulate the BRAINBOX® ETHERNET System on one PC with network functionality and at the same time design the EEG-monitor software on a other PC and test this software against the BRAINBOX® Protocol. First this tool was designed for internal use. But with a number of changes and remove special functions a tool is created for customer use. On this way a user can get to know the BRAINBOX® ETHERNET System without the need to have the actual hardware. At the same time it can be used with BRAINTRONICS demonstration platform the BRAINBOX® TCP/IP EEG-Monitor which acts as a simple EEG acquisition application.
For users that make their own tool for presentation of EEG-data and control of the ETHERNET 102 (V2) INTERFACE this virtual amplifier can be used during software design. It responds on the same way to the basic commands described in the BRAINBOX® Protocol network interface document and generates data patterns.
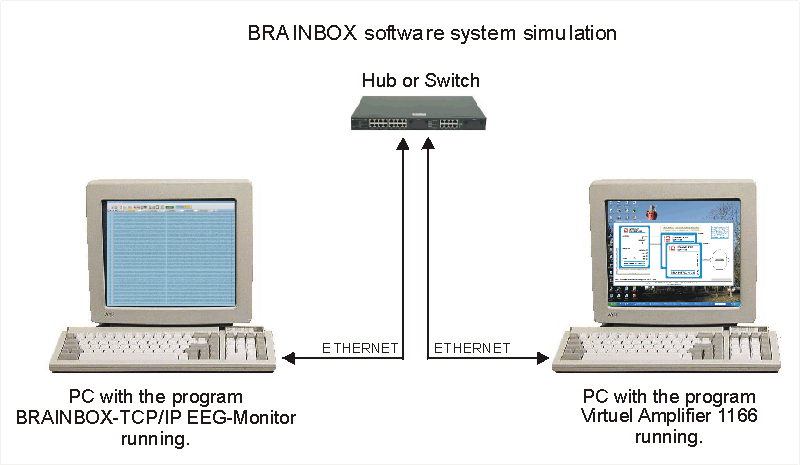
The PC configuration can look like the figure below. In this example the configuration consists of two PC’s and a hub or switch. In principle it is also possible to connect the two PC’s directly with a cross-cable. The hub or switch can be omitted then. It is also possible, provided that the PC is fast enough, to run both applications on the same PC. The communication between the two programs is still by means of the TCP/IP protocol. The only difference is the lack of the physical ETHERNET interface.
The Virtual Amplifier is a server application, which can be approached by means of the TCP/IP protocol via a physical ETHERNET connection. After program start, the server becomes active and will listen on the network link if there is an active client (BRAINBOX® TCP/IP EEG-Monitor program) to make a connection with. If the client indicates that it wants to make a connection, the server will permit this and on both sides of the network a visible Connect-indication is given. The exchange of data between the server and the client goes by means of the TCP/IP protocol. In the data field of the ETHERNET frame the BRAINBOX® protocol is packed allowing the two PC applications to talk with each other and carry out tasks. This BRAINBOX® protocol is described in the document “ BRAINBOX® Protocol network interface” document.
The above is reflected in a diagram below.
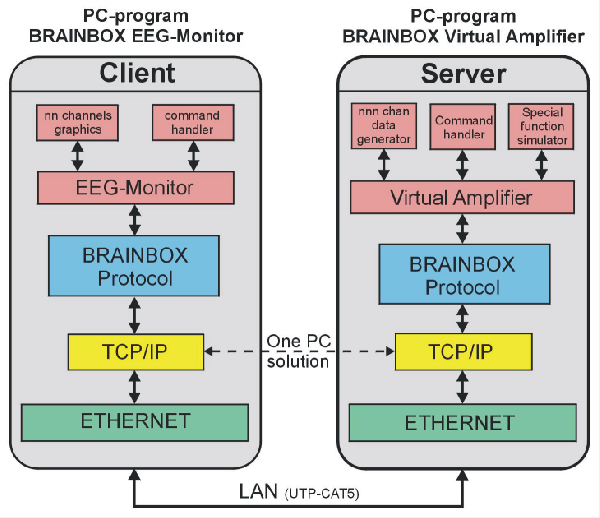
The Virtual Amplifier is able to carry out the basic commands of the BRAINBOX® protocol. For EEG simulation the Virtual Amplifier in fact is a data generator, which can generate a range of signals. The data is packed in the same data frame as by the real ETHERNET-102 (V2) INTERFACE. The Virtual Amplifier can produce these signals infinitely. Further the Virtual Amplifier can simulate a number of special functions for fault simulation, digital I/O, DC-channels, Nonin Pulse Oximeter and Event.
The data pattern, which is produced, depends on the configuration, which is send by the EEG-Monitor software to the Virtual Amplifier in a configuration frame. So it can be simulating at one moment a 256-channel system and after sending a new configuration it simulates a single 42-channel amplifier. As extra the Virtual Amplifier offers the possibility to “play-back” a previously recorded real EEG-data sample and generate this as an ongoing pattern to the client application.
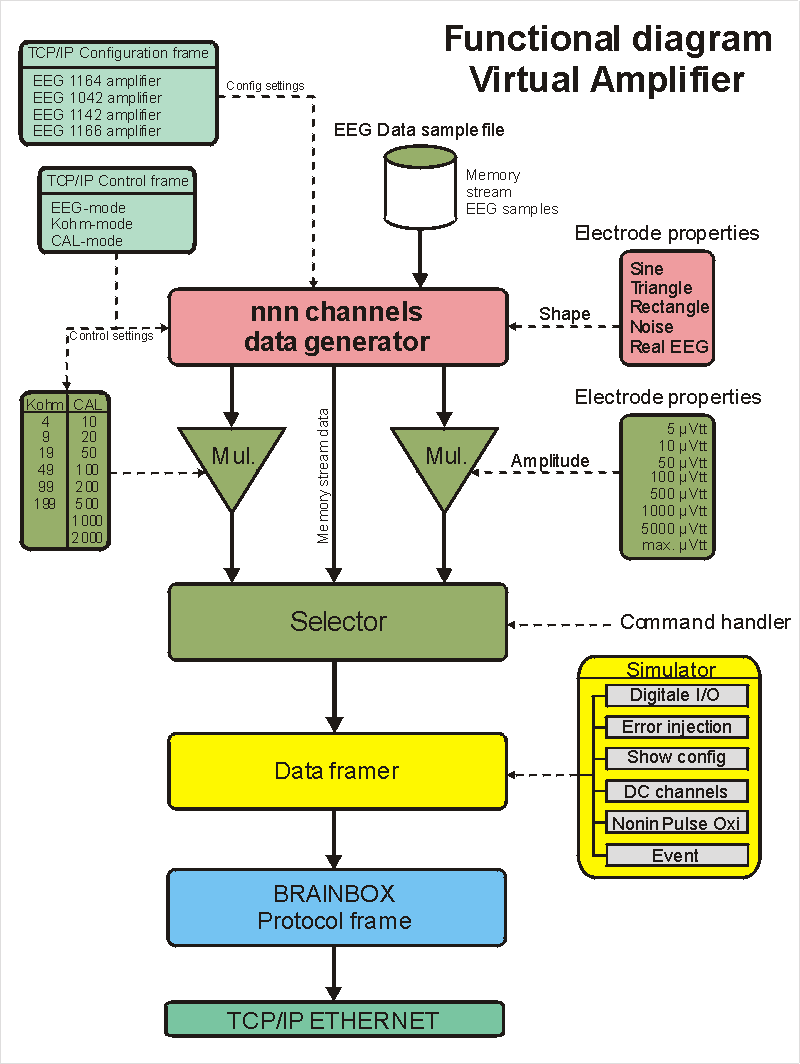
Functional diagram Virtual Amplifier.
The Virtual amplifier has functionally been built as reflected in Figure below.
At the top of the diagram the data generator is seen. The signal shape of the data generator can be controlled via the electrode properties. At this level the choice is also made for the EEG, Kohm, CAL signal function (by means of the control frame) and for the external EEG sample signal.
As the data generator is loaded on specification of the electrode properties, the amplitude is established there. If has been chosen for Kohm or CAL that the signal is controlled by means of the command handler. The command handler gets its tasks from the EEG-Monitor program via the control frames. If real EEG data samples are generated, the amplitude of the signal is defined in de data file and the data is not going through the multiplier. The selector decides which signal path is chosen by means of the state of the command handler and the electrode properties. (the green blocks reflect this function)
Now the data frame will be built and, if needed, a number of bit simulations take place such as: error injection, plug/device events, digital I/O, DC-channels, Pulse Oximeter and events.
At the end the data frame is placed in the BRAINBOX® protocol frame and the data is send by means of the TCP/IP protocol over ETHERNET.